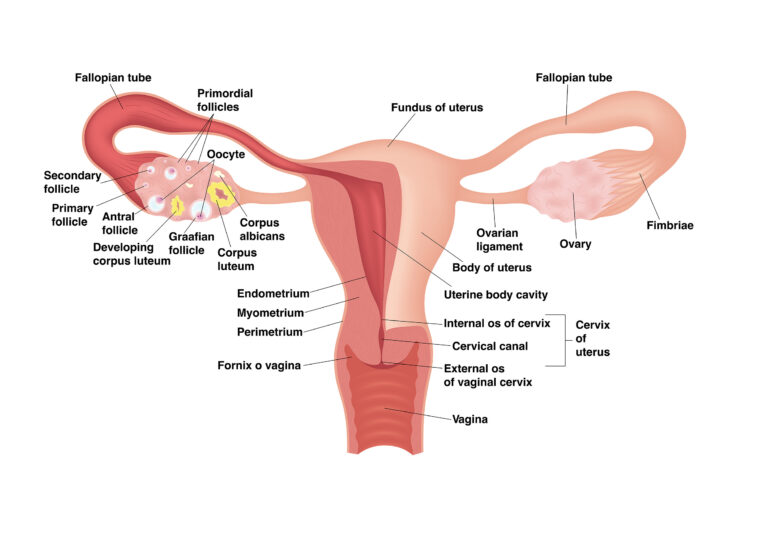
what are the symptoms of endometriosis after menopause?
Endometriosis does not “die off” or go away with a hysterectomy or menopause. Some people do find some relief from their symptoms, but endometriosis can still persist. Endometriosis often has several related or comorbid conditions (such as adenomyosis or fibroids) that share similar symptoms (pain with menstruation, chronic pelvic pain, etc.) that a hysterectomy might help – but it may not stop your symptoms from endometriosis. Endometriosis exists outside of the uterus and can still respond to hormonal influences (Bulun et al., 2002). Even if your ovaries are removed, endometriosis lesions can produce their own estrogen (Huhtinen et al., 2012). This is important to note because estrogen causes endometriosis lesions to grow and persist (Bulun et al., 2012). So even with the removal of the ovaries or with menopause, endometriosis can sustain itself.
There is high recurrence of symptoms with the removal of just the uterus; but, even with the removal of the ovaries, any endometriosis lesions left behind can continue to grow, progress, and cause symptoms (Clayton et al., 1999; Inceboz, 2015; Khan et al., 2013; Rizk et al., 2014). So, if you have your uterus and ovaries removed for other conditions, it is best that all endometriosis lesions be removed as well. The skill of the surgeon at removing all endometriosis is important. Rizk et al. (2014) report that “the recurrence of endometriosis symptoms and pelvic pain are directly correlated to the surgical precision and removal of peritoneal and deeply infiltrated disease.”
Endometriosis has been found in about 2.2% of postmenopausal women (Zanello et al., 2019). Inceboz (2015) states that “endometriotic lesions remained biologically active, with proliferative activity and preserved hormonal responsiveness, even in the lower estrogenic environment in the postmenopause.” Postmenopausal endometriosis should be managed surgically according to Streuli et al. (2017) and Zanello et al. (2019).
What about hormone replacement if you are in menopause or have had your uterus and ovaries removed? Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is important as “the hypo-estrogenic state was demonstrated to be a risk factor for cardiovascular and bone disease” (Zanello et al., 2019). While HRT has not been concluded useful for preventing heart disease, it can be useful for those at a higher risk of osteoporosis (Zanello et al., 2019). There isn’t much data available to help guide the decision, but Zanello et al. (2019) report that “in young menopausal women with premature or surgically-induced menopause the benefits of HRT probably overcome the risks” and “in women with residual endometriosis after surgery, the use of HRT should be discussed and the risk of recurrence should be carefully considered before starting an estrogen-based replacement therapy”. Rizk et al. (2014) also states that “the general consensus is that the benefits outweigh the risks” and that starting HRT soon after menopause does not seem to have a faster rate of recurrence. Zanello et al. (2019) concludes that “based on low-grade evidence in the literature, we recommend prescribing combined HRT instead of unopposed estrogen.” It also depends on if your endometriosis was removed.
Does Endometriosis Go Away After Menopause?
endometriosis symptoms after menopause
References
Bulun, S. E., Gurates, B., Fang, Z., Tamura, M., Sebastian, S., Zhou, J., … & Yang, S. (2002). Mechanisms of excessive estrogen formation in endometriosis. Journal of reproductive immunology, 55(1-2), 21-33. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-0378(01)00132-2
Bulun, S. E., Monsavais, D., Pavone, M. E., Dyson, M., Xue, Q., Attar, E., … & Su, E. J. (2012, January). Role of estrogen receptor-β in endometriosis. In Seminars in reproductive medicine (Vol. 30, No. 01, pp. 39-45). Thieme Medical Publishers. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4034571/…
Clayton, R. D., Hawe, J. A., Love, J. C., Wilkinson, N., & Garry, R. (1999). Recurrent pain after hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo‐oophorectomy for endometriosis: evaluation of laparoscopic excision of residual endometriosis. BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology, 106(7), 740-744. Retrieved from https://obgyn.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1471-0528.1999.tb08377.x?fbclid=IwAR04aFoLsukqsYutNPNXtJNZpKLNEJbgOOon334NW8D7wvwzZMWaS2YaZts
Huhtinen, K., Ståhle, M., Perheentupa, A., & Poutanen, M. (2012). Estrogen biosynthesis and signaling in endometriosis. Molecular and cellular endocrinology, 358(2), 146-154. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0303720711005041
Inceboz, U. (2015). Endometriosis after menopause. Women’s Health, 11(5), 711-715. Retreived from https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.2217/whe.15.59
Khan, K. N., Kitajima, M., Fujishita, A., Nakashima, M., & Masuzaki, H. (2013). Toll‐like receptor system and endometriosis. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research, 39(8), 1281-1292. Retrieved from https://obgyn.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/jog.12117
Rizk, B., Fischer, A. S., Lotfy, H. A., Turki, R., Zahed, H. A., Malik, R., … & Herrera, D. (2014). Recurrence of endometriosis after hysterectomy. Facts, views & vision in ObGyn, 6(4), 219. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4286861/
Zanello, M., Borghese, G., Manzara, F., Degli Esposti, E., Moro, E., Raimondo, D., … & Seracchioli, R. (2019). Hormonal replacement therapy in menopausal women with history of endometriosis: a review of literature. Medicina, 55(8), 477. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6723930/